A black swift nesting (Photo by Aaron Maizlish, CC-BY-NC).
Black swift
Black swift is a high-flying, elusive bird that nests on steep cliffs in BC and Alberta. During breeding season, Canada is home to about 80 per cent of the North American population of this bird species.
What does the black swift look like?
Black swift is the largest bird in the swift family, measuring about 18 centimetres in length for adults. It has black plumage and a long, slender body with crescent-shaped wings and a notched tail.
Where does the black swift live?
Preferring vertical cliffs, in canyons or on the coast, black swift nests on damp rocks behind waterfalls and near streams. It builds its nest under the covering of overhangs or crevices.
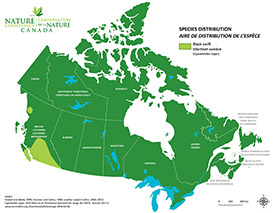
Black swift has a summer breeding range across northwestern BC, southwestern Alberta and the northwestern U.S., with scattered populations through the southwestern U.S., Mexico and the Caribbean. This species migrates to spend winters in South America.
What does the black swift eat?
Black swift feeds exclusively on flying insects, including winged ants, wasps, flies and beetles. This species forages while flying, scooping insects into its wide bill.
How does the black swift behave?
Aerial foragers, black swift may cover hundreds of kilometres in a single day to feed, flying at heights not visible from the ground. Black swift has been difficult to study due to its remote nests and long-distance foraging. The first black swift nest was not documented until 1901 in California.
Black swift lays a single egg and builds its cup-shaped nests out of mud and plants, often adding material to reuse over the years. Both parents care for their young, which will learn to fly after 1.5 months.
What is the black swift's conservation status?
In 2015, this species was designated as endangered by the Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada. The Canadian population appears to have declined by more than 50 per cent between 1973 and 2012. This decline may be a result of declining insect populations.
What is NCC doing to help protect the black swift's habitat?
The Nature Conservancy of Canada (NCC) protects habitat within the range of black swift in Alberta and BC. Black swift has been observed in the Rocky Mountain Trench in southeastern BC, where NCC has numerous conservation areas, including Columbia Lake-Lot 48 and Pine Butte Ranch.